Zirconium radioactive decay
The half-lives of all other isotopes are less than three months. Zirconium -93 decays by emitting a beta particle with a half-life of 1. Most of the isotope data on this site has been obtained from the National Nuclear Data Center. Please visit their site for more information. Radioactive Isotopes: 29 Stable Isotopes: 4 Total Isotopes: 41 Atomic Symbol: Zr Nuclear Levels Associated with Zirconium 95 and Niobium 95 link.
To perform the Yttrium- Zirconium separation, a column is packed with the resin and.
Isotopes of the element zirconium
International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Zr, which decays by positron emission (23%) and electron capture. Zirconia and zirconium are not radioactive So, there are no radioactive traces in items like dental implants, biomedical implants and jewellery made from cubic zirconia. Is zircon or zircon sand radioactive? What was zirconium used for in the past? It is also highly resistant to corrosion.
Zirconium and its alloys have been used for centuries in a wide variety of ways.
Selective resonance photoionization of odd mass zirconium
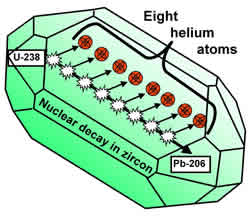 What is the most common isotope of zirconium? Zr is the least common, comprising only 2. Uranium -238 decays by alpha emission into thorium-234, which itself decays by beta emission to protactinium-234, which decays by beta emission to uranium -234, and so on. The various decay products, (sometimes referred to as “progeny” or “daughters”) form a series starting at uranium -238. Uranium: Its Uses and Hazards – Institute for Energy and. Căutați: What does uranium decay into? The existence of a long half-life radioactive zirconium isotope. At the University of Missouri, researchers have done just that by revealing the largely unexplored potential of radioactive isotopes. Traducerea acestei pagini 5 feb. Management of Radioactive Waste from the Mining and Milling of Ores. U decay series radionuclides in zircon and zirconia are such that, in terms of. Radioisotopic dating relies on the process of radioactive decay, in which the.
What is the most common isotope of zirconium? Zr is the least common, comprising only 2. Uranium -238 decays by alpha emission into thorium-234, which itself decays by beta emission to protactinium-234, which decays by beta emission to uranium -234, and so on. The various decay products, (sometimes referred to as “progeny” or “daughters”) form a series starting at uranium -238. Uranium: Its Uses and Hazards – Institute for Energy and. Căutați: What does uranium decay into? The existence of a long half-life radioactive zirconium isotope. At the University of Missouri, researchers have done just that by revealing the largely unexplored potential of radioactive isotopes. Traducerea acestei pagini 5 feb. Management of Radioactive Waste from the Mining and Milling of Ores. U decay series radionuclides in zircon and zirconia are such that, in terms of. Radioisotopic dating relies on the process of radioactive decay, in which the.
In the magma, crystals of zirconium silicate (called zircons), as well as other . ZrO2) leads to incorporation of some radionuclides into. A curie is a unit of measure of the rate of radioactive decay equal to 3. The odd-mass zirconium isotopes (93 and 95) are among fission products that are radioactive.
Notably, the 93 Zr isotope reveals a long half-life .
Naturally-occurring radioactive materials and the regulatory
 Mueller calls “the clock within the zircon ” because it converts to the element lead at a specific rate over . Zirconium is a bone seeker and demetallation can lead to increased radiation. Although the radioactive decay of a nucleus is too small to see with the naked eye.
Mueller calls “the clock within the zircon ” because it converts to the element lead at a specific rate over . Zirconium is a bone seeker and demetallation can lead to increased radiation. Although the radioactive decay of a nucleus is too small to see with the naked eye.
It does not corrode at high temperatures, nor absorb neutrons to form radioactive isotopes. Even today the nuclear industry buys almost all of the metal that is .
 International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Zr, which decays by positron emission (23%) and electron capture. Zirconia and zirconium are not radioactive So, there are no radioactive traces in items like dental implants, biomedical implants and jewellery made from cubic zirconia. Is zircon or zircon sand radioactive? What was zirconium used for in the past? It is also highly resistant to corrosion.
International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Zr, which decays by positron emission (23%) and electron capture. Zirconia and zirconium are not radioactive So, there are no radioactive traces in items like dental implants, biomedical implants and jewellery made from cubic zirconia. Is zircon or zircon sand radioactive? What was zirconium used for in the past? It is also highly resistant to corrosion.